How Do Retroviruses Differ From So-called Ordinary Viruses
So-called endogenous retroviruses ERVs are persistent features of the genomes of many animals. Sometimes however a virus will infect a germ cell delivering its genetic material to a sperm or egg.
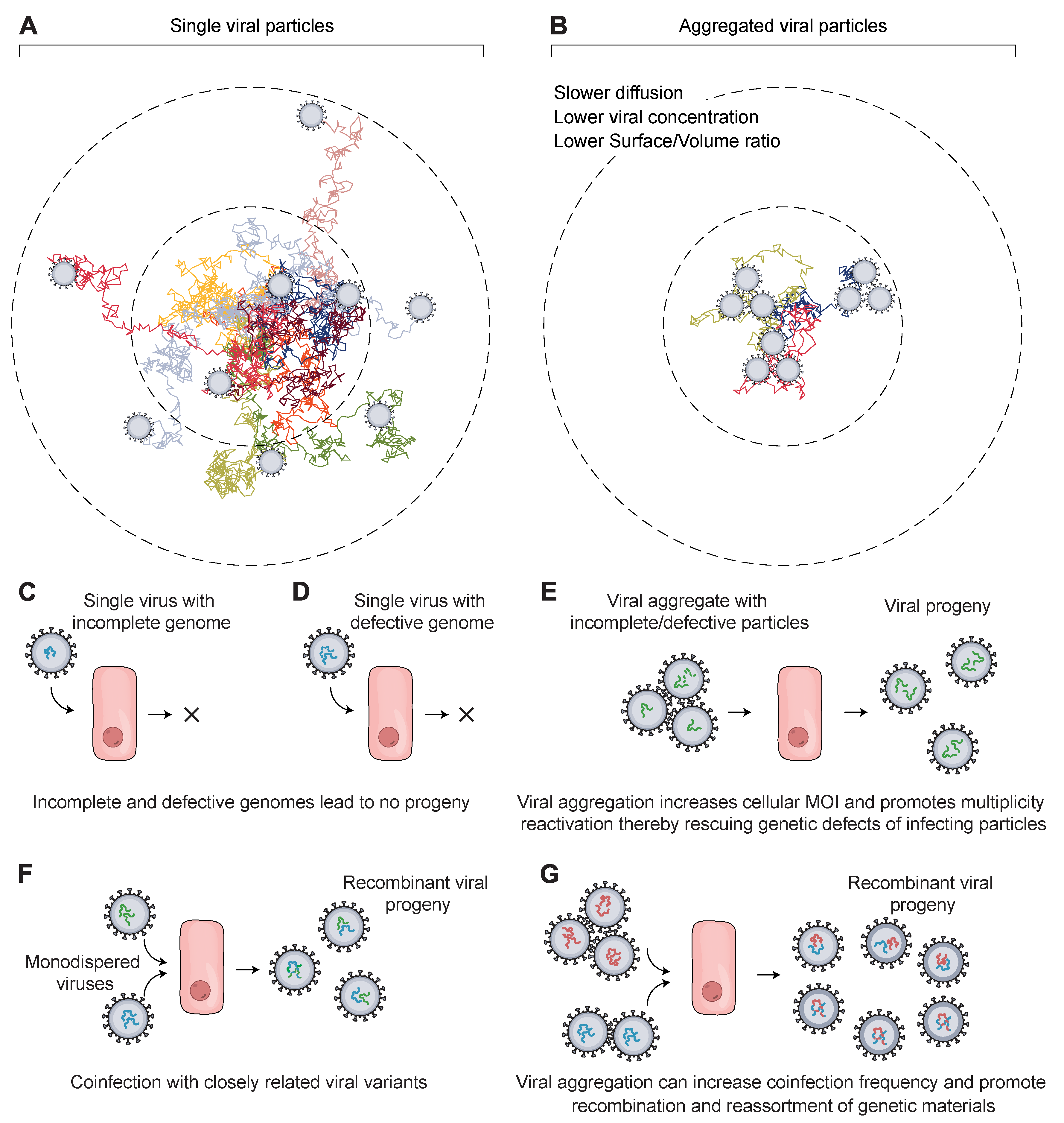
Viruses Free Full Text Viral Aggregation The Knowns And Unknowns Html
So-called endogenous retroviruses make up 8 percent of the human genome.

. The polydnaviruses circular DNA viruses are fused into their host genomes as endogenous DNA viruses of some parasitoid wasps essential for survival of the wasp. Animal viruses do not always express their genes using the normal flow of genetic informationfrom DNA to RNA to protein. Instead some become chronic.
The Characteristics of Retroviruses. Retroviruses are a group of viruses so retroviruses carry special characteristics which are not seen in viruses. When an ordinary retrovirus infects a cell it inserts its genes into the cells DNA.
Human ERVs HERVs have become distributed within human DNA over. These silent genes can activate when our immune response is weakened setting off new rounds of viral replication. It was established quite early that retroviruses do have the ca pacity to cause tumors at least in the laboratory.
Viral proteins on the capsid or phospholipid envelope interact with. Respiratory viruses get into the airway and spread via coughing sneezing or breathing. The nature of the genome determines how the genome is replicated and.
He showed that the virus-now called avian sarcoma virus-can in. Like other viruses retroviruses need to use the cellular machinery of the organisms they infect to make copies of themselves. A bacterium is a living thingmost of them have all of the components they need for their own survival for making more of themselves and so on.
The cell uses some of those RNA molecules to make proteins for the virus. Well go over how their replication process differs which retroviruses affect humans and. The cell then makes new retroviruses by making a copy of the viruss genes as RNA molecules.
The first retrovirus was isolated in J 91 0 by Peyton Rous of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Re search. Once it has infected a cell it converts its RNA into DNA by reverse transcription. For example the baculovirus Autographa californica MNP virus AcMNPV has acquired a gypsy-like retrovirus eg TED an endogenous retrovirus associated with moth development.
There are more than 30 kinds but only three or four affect people. When a retrovirus infects a cell it makes a DNA copy of its genome that is inserted into the DNA of the host cell. Different viruses do their best or worst work in specific cell types and mostly they stay more or less where theyre expected to be.
There are a variety of different retroviruses that cause human diseases such as some forms of cancer and AIDS. When an ordinary retrovirus like HIV infects a cell it inserts its genes into the cells DNA. Retroviruses are viruses with RNA as genetic material.
Conversely viruses are also full of DNA sequences that attract molecules which switch genes on. In a functional retrovirus these switches activate the viral genes so it can become infectious again. But when a virus-like sequence gets spliced into another region in the genome this ability to act as a genetic switch can end up going rogue.
Retroviruses cause tumour growth and certain cancers in animals and are associated with slow infections of animals such as equine infectious anemia. Viruses dont always kill the cells they take hostage. The cell then makes new retroviruses by.
ERVs consist of the genetic material of extinct or fossil viruses the genomic constitution of which is similar to that of extant retroviruses. Retroviruses have various characteristics that make them unique as gene delivery vehicles. The coronavirus is the cause of about 20 of colds.
Retroviruses are the only animal viruses that integrate into the host cells genome during the normal growth cycle. Because the introduction of the retrovirus was still so new the virus hasnt accumulated many mutations and the koalas genetic machinery still actively turns the viral DNA into active virus. A retrovirus is a virus whose genes are encoded in RNA and using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase replicates itself by first reverse-coding its genes into the DNA of the cells it infects.
The cell uses some of those RNA molecules to make proteins for the virus. These tend to do their dirty work in the winter and early spring. A retrovirus is a type of virus that replicates differently than traditional viruses do.
A retrovirus is a virus that uses RNA as its genetic material. When that happens. Their life cycle includes an integrated state in the DNA of the host chromosome.
Although the replicative life cycle of viruses differs greatly between species and category of virus there are six basic stages that are essential for viral replication. A virus puts its information into a cella bacterial cell a human cell or animal cell for. When an ordinary retrovirus like HIV infects a cell it inserts its genes into the cells DNA.
They belong to the family Retroviridae of Retroviruses. A virus is just a piece of information. Retroviruses would ever be found in human beings.
However others may have ssDNA dsRNA or ssRNA genomes. This viral DNA is then inserted into the DNA of the host cell where it starts replicating. The cell then makes new retroviruses by making a copy of the viruss genes as RNA molecules.
Viruses are completely different from bacteria. In humans a retrovirus known as human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 HTLV-1 causes a form of cancer called adult T-cell leukemia ATL. When an ordinary retrovirus like HIV infects a cell it.
As viruses are obligate intracellular pathogens they cannot replicate without the machinery and metabolism of a host cell. Virus contains genetic material as DNA or RNA but retrovirus contains only RNA. For eg Human Immunodeficiency Virus HIV.
Some viruses have a dsDNA genome like cellular organisms and can follow the normal flow. It can also cause a neurodegenerative condition known as HTLV-1-associated. So-called retroviruses such as HIV sew their genes into the genome of the cells theyve invaded.
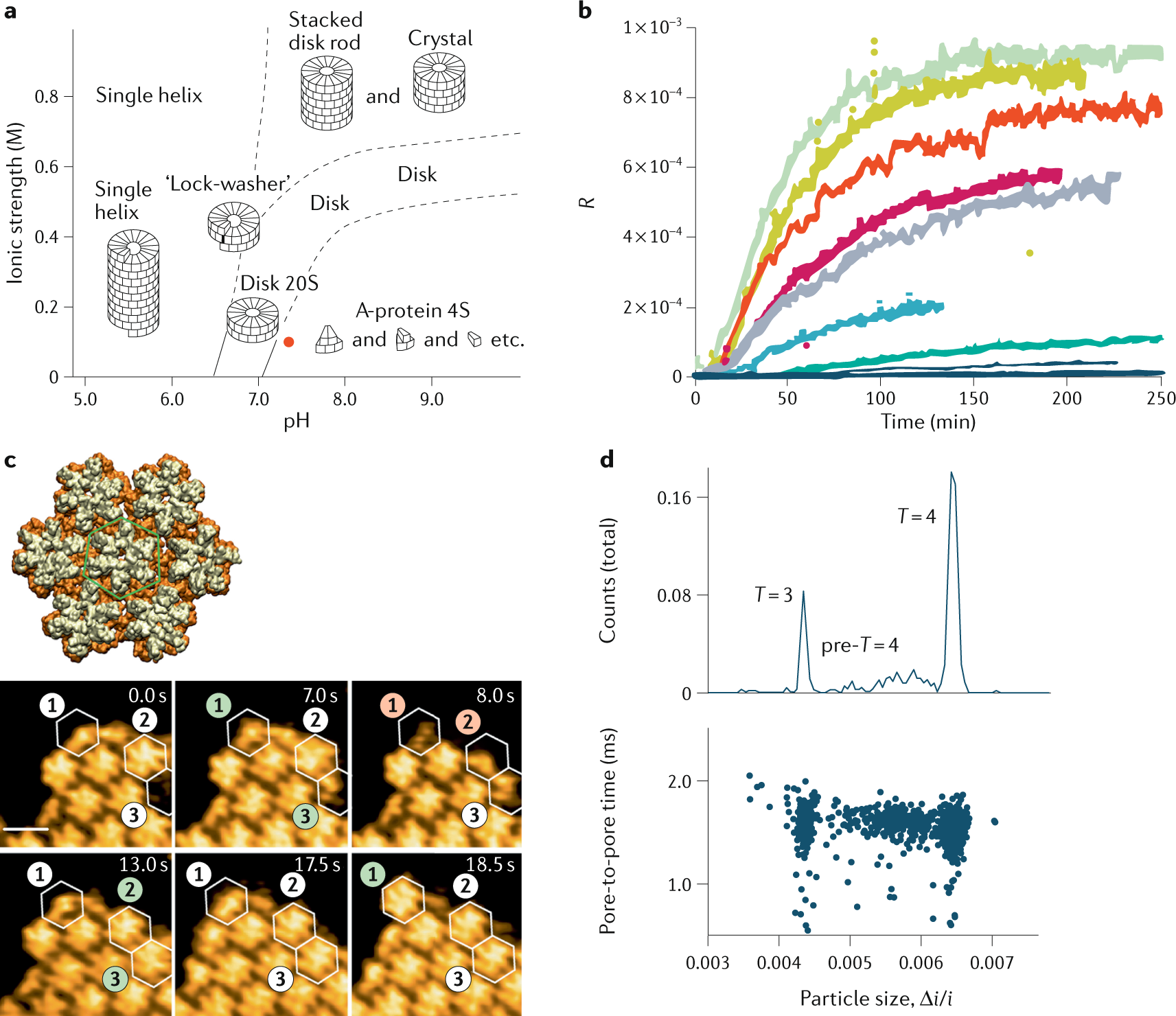
Physics Of Viral Dynamics Nature Reviews Physics
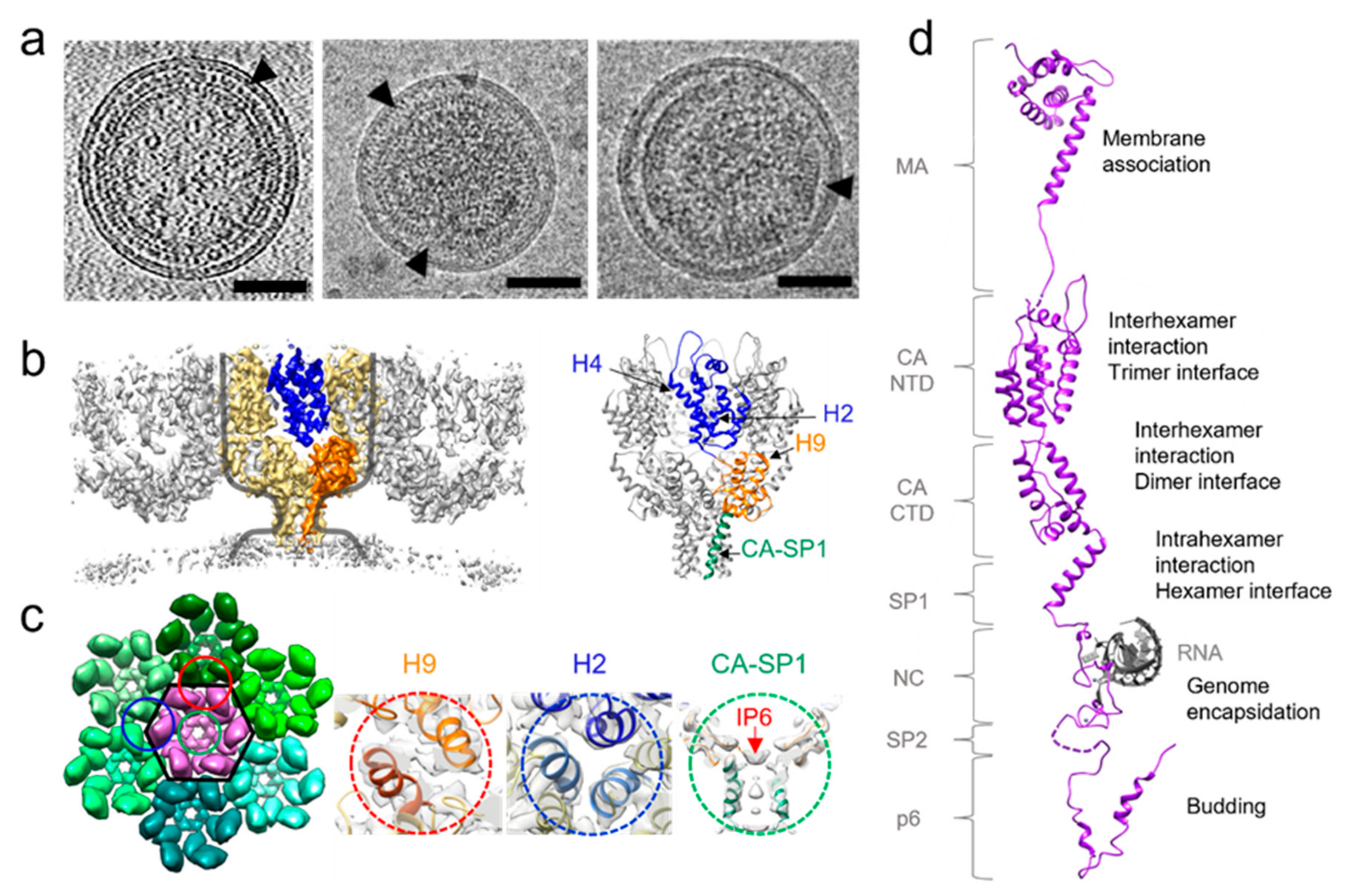
Viruses Free Full Text Structural Analysis Of Retrovirus Assembly And Maturation Html
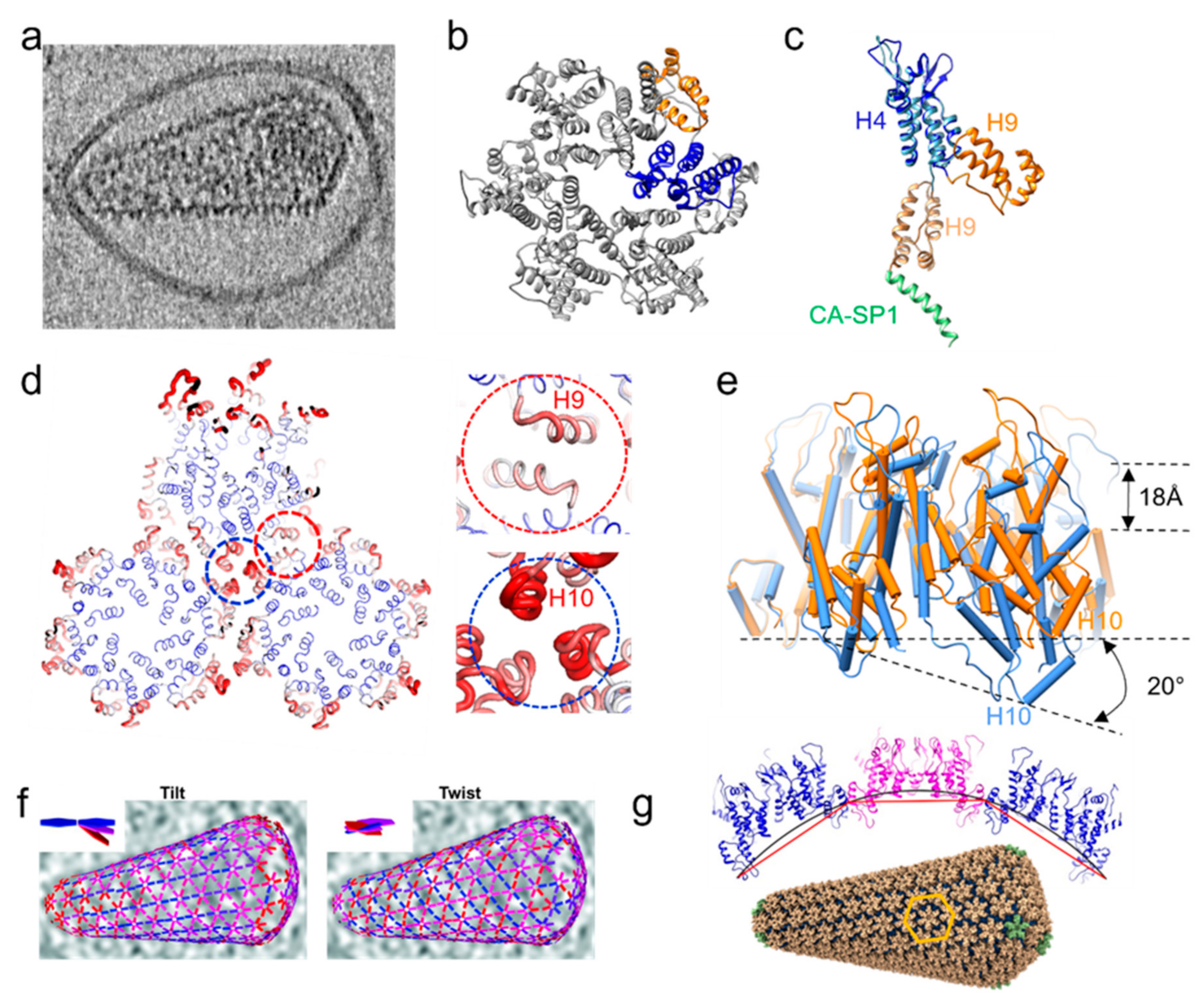
Viruses Free Full Text Structural Analysis Of Retrovirus Assembly And Maturation Html
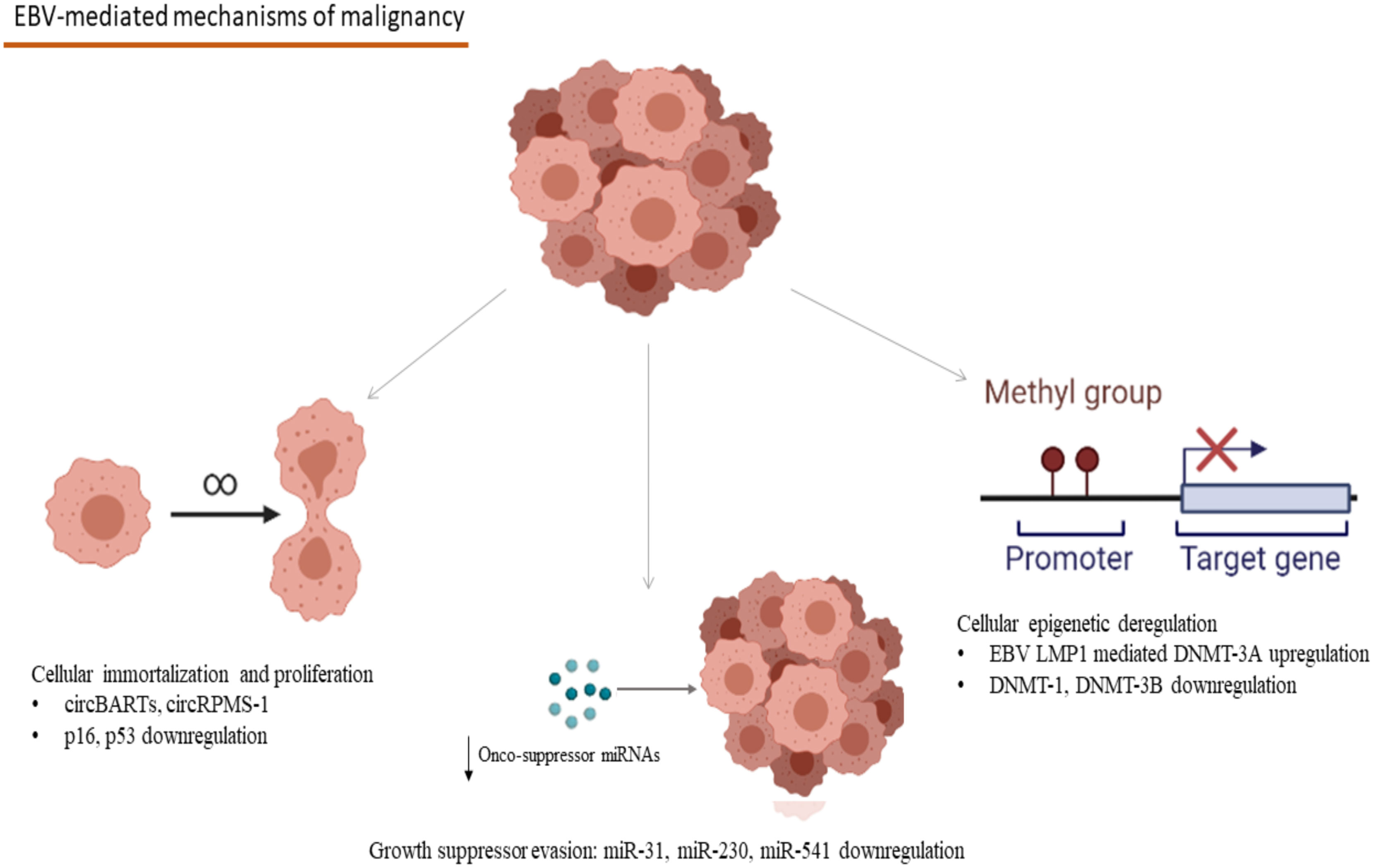
Frontiers Viral Causality Of Human Cancer And Potential Roles Of Human Endogenous Retroviruses In The Multi Omics Era An Evolutionary Epidemiology Review Oncology
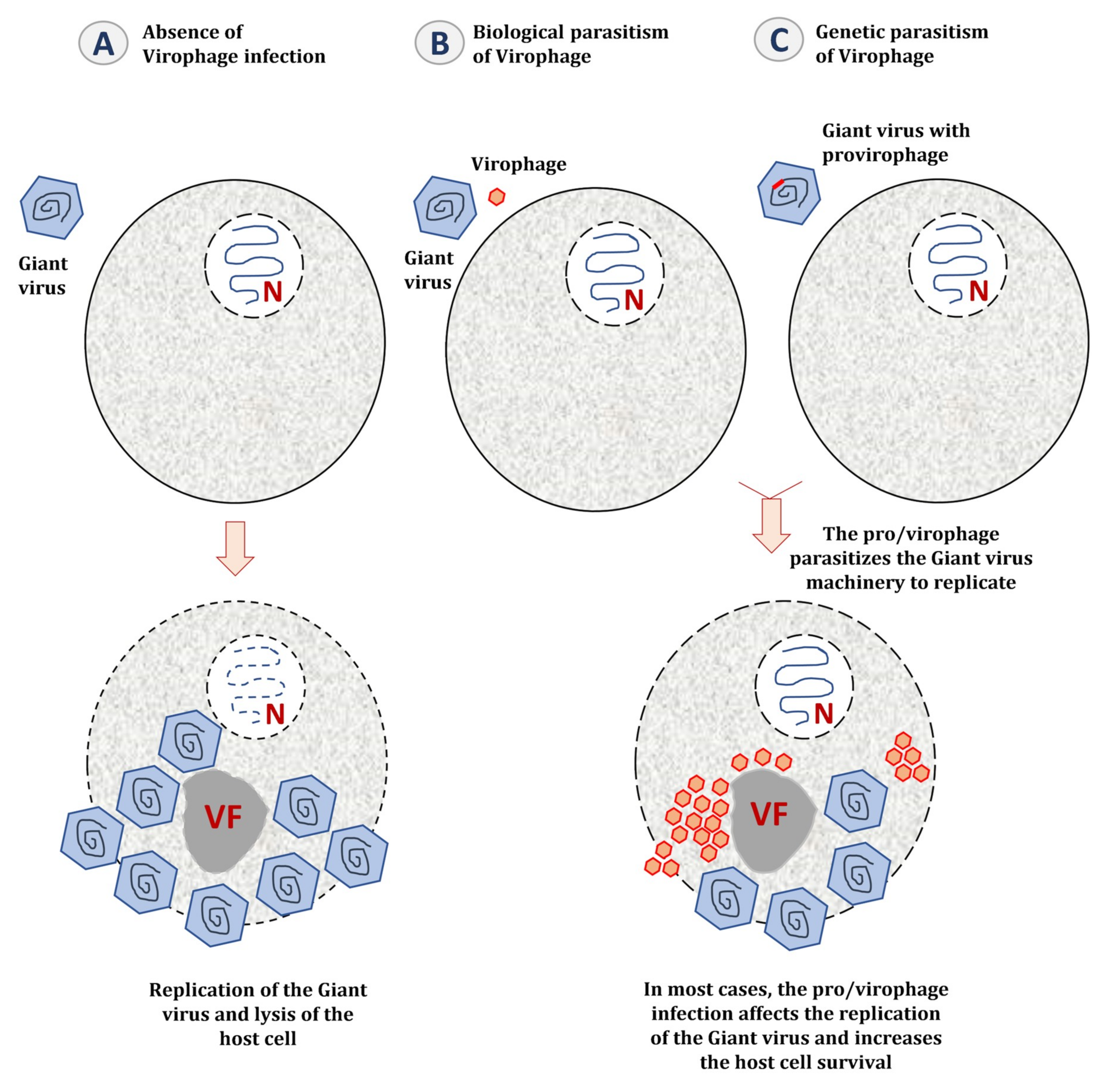
Viruses Free Full Text Virophages Of Giant Viruses An Update At Eleven Html
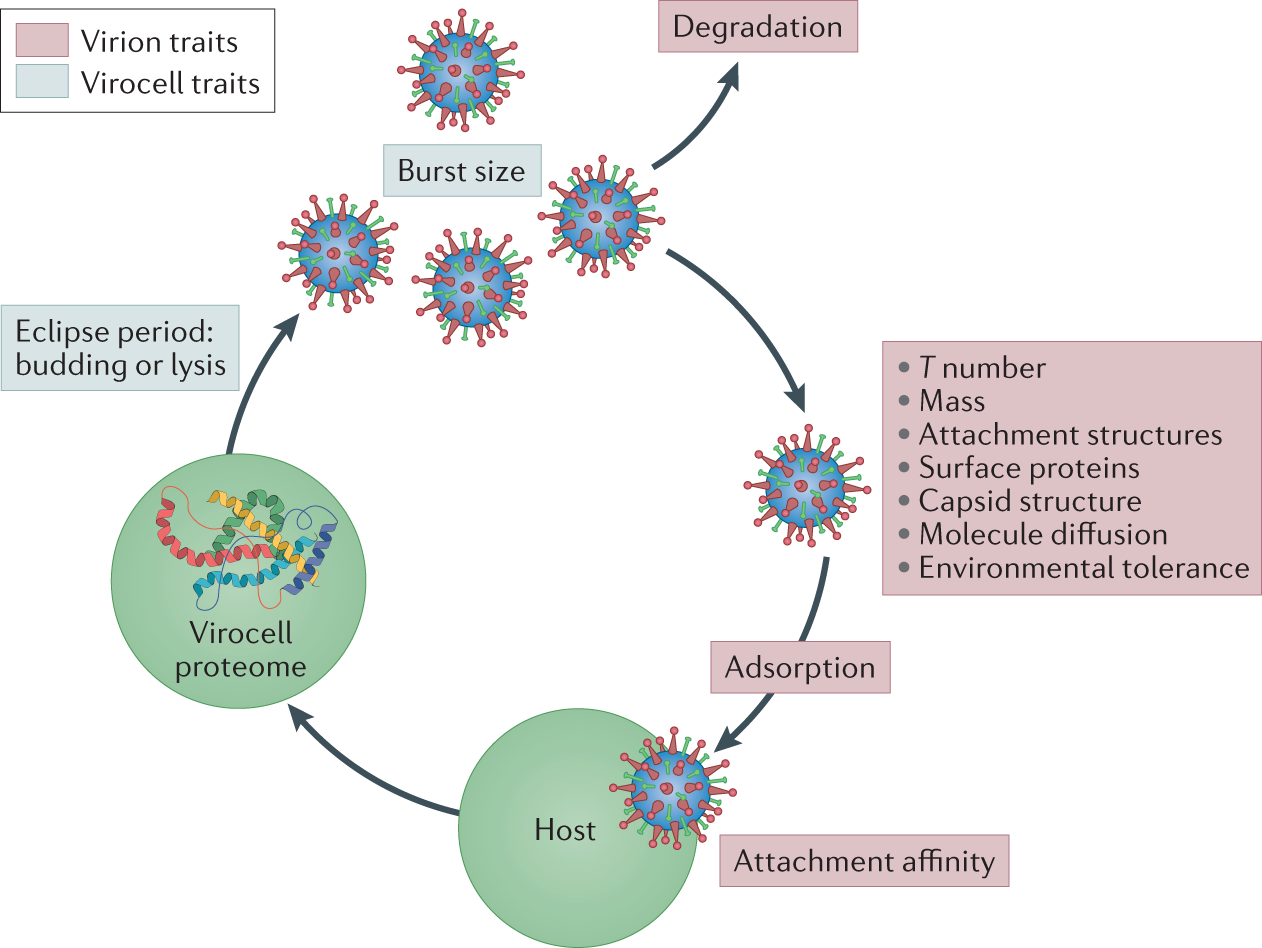
Towards An Integrative View Of Virus Phenotypes Nature Reviews Microbiology

Retroviruses An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Viral Clearance Studies For The Biopharmaceutical Industry Bioprocess Internationalbioprocess International

Dna Viruses An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Retrovirus Definition Examples Diseases Replication Facts Britannica

Viruses As Truffle Hounds Molecular Tools For Untangling Brain Cellular Pathology Trends In Neurosciences

Virus Genome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
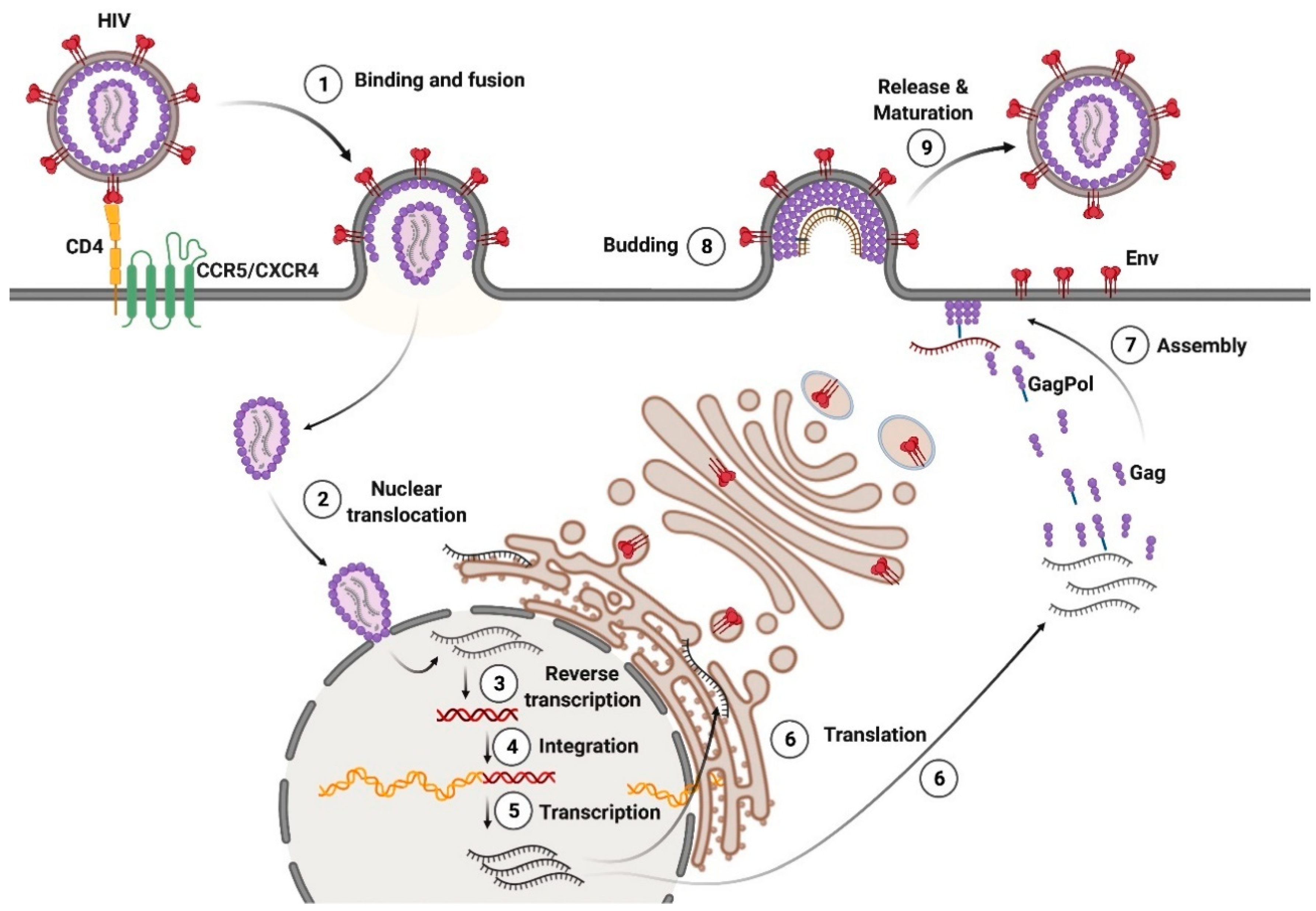
Viruses Free Full Text Hiv 1 And Htlv 1 Transmission Modes Mechanisms And Importance For Virus Spread Html

Retroviridae An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
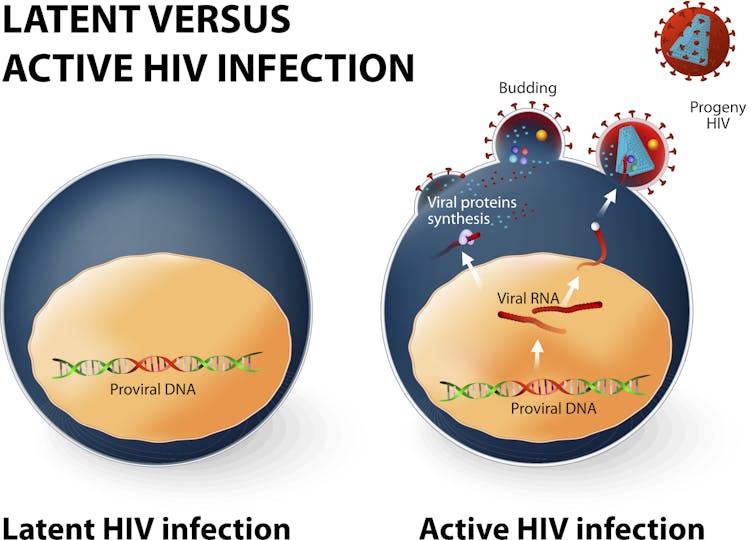
Does Coronavirus Linger In The Body What We Know About How Viruses In General Hang On In The Brain And Testicles Jakarta Berketahanan

Virus Genome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
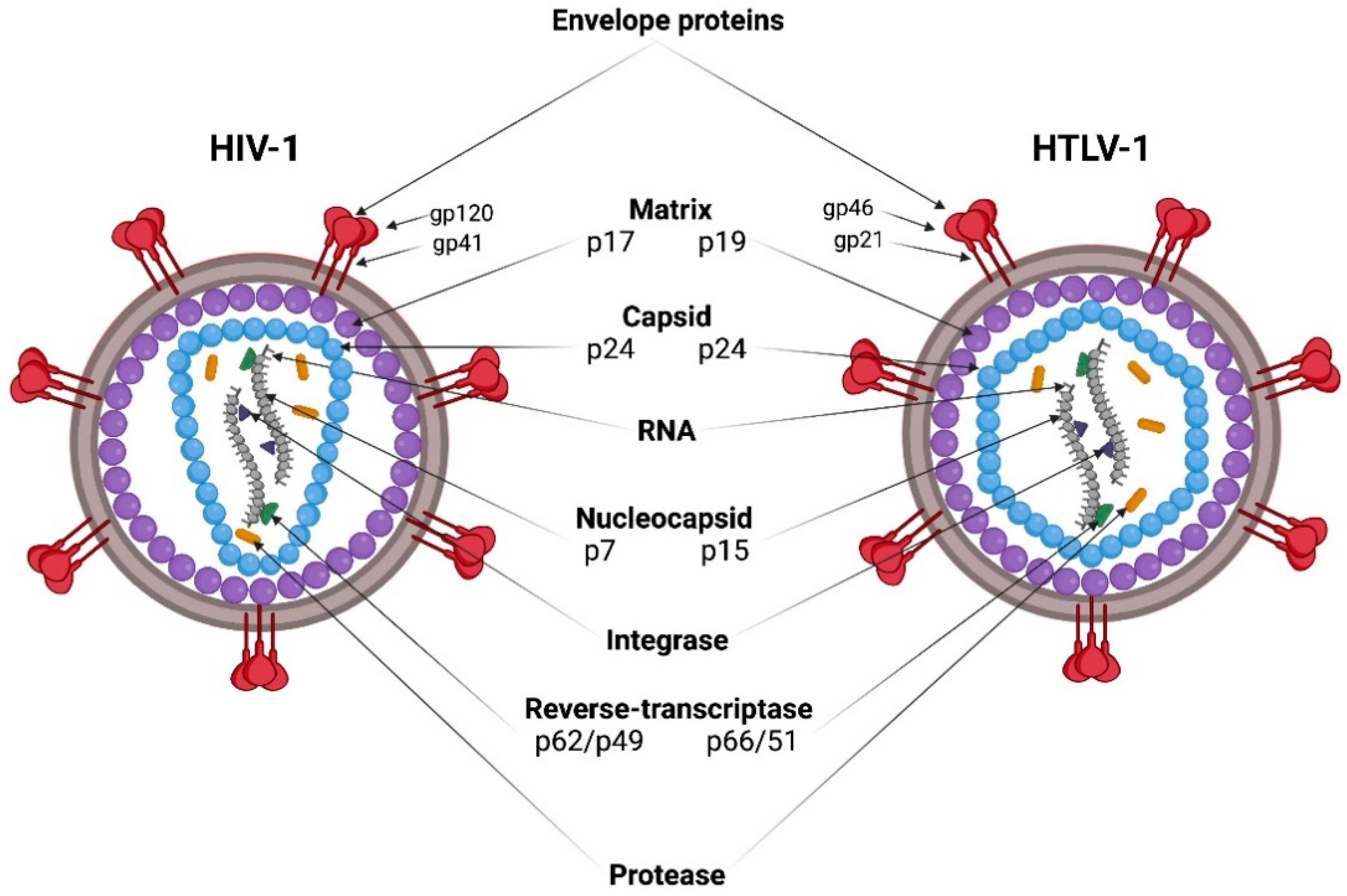
Viruses Free Full Text Hiv 1 And Htlv 1 Transmission Modes Mechanisms And Importance For Virus Spread Html

Retrovirus Definition Examples Diseases Replication Facts Britannica
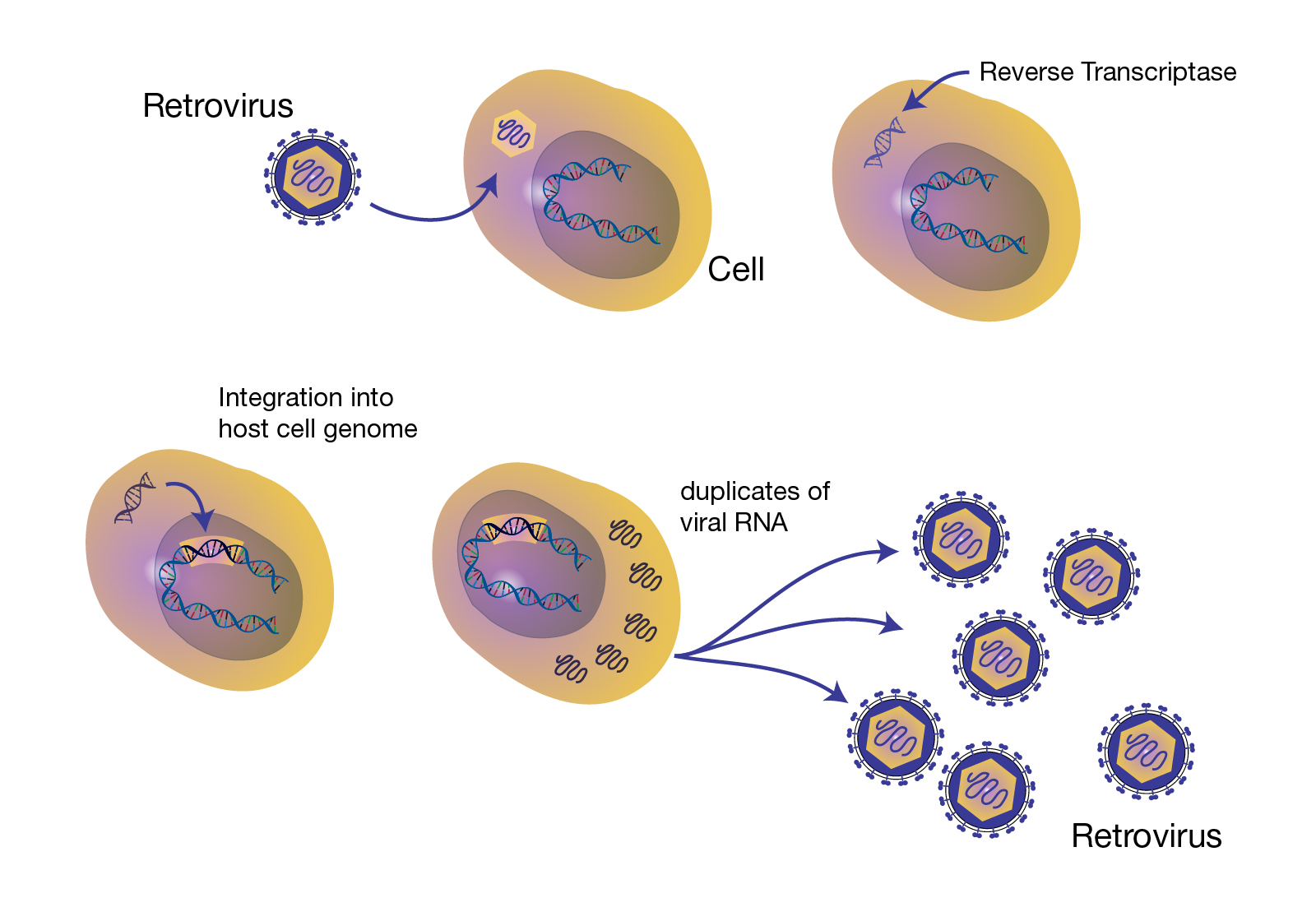
Comments
Post a Comment